Roofing Terms
Main Roof Components
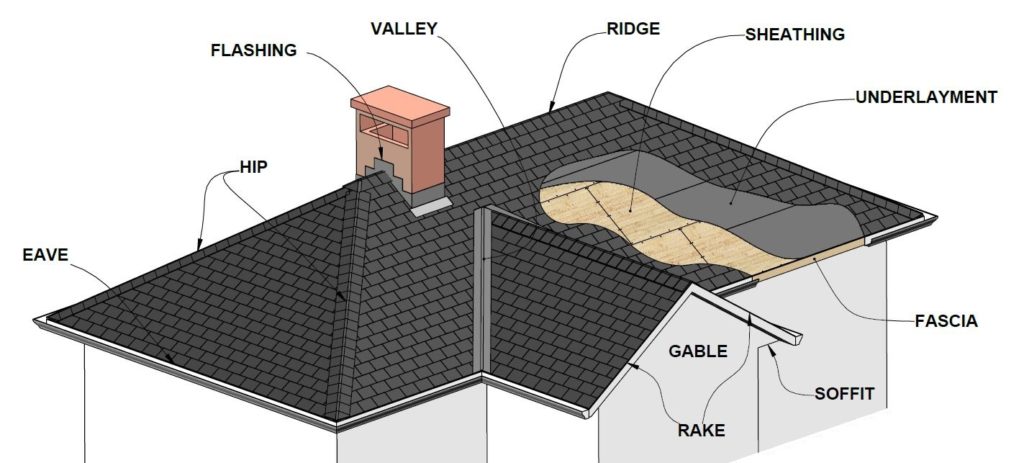
Terms Used by Roofers
Deck: The structural nailing base for the roof surface, usually composed of plywood sheathing and underlayment.
Drip Edge: A type of flashing made of thin strips of metal that extend the length of eaves and rakes to facilitate water runoff.
Eave: The edge of the roof that projects beyond the house wall.
Fascia: Wood or other trim covering the ends of the rafters.
Flashing: Waterproofing materials, usually metal, that connect roof shingles to chimneys, valleys, vent pipes, vertical walls, eaves and rakes.
Gable: A type of roof with two slopes meeting at a horizontal ridge. Also, the triangular area formed by such a roof.
Rake: The edge of a pitched roof at the gable end.
Ridge: The top edge of the roof, where two slopes meet in a horizontal line.
Sheathing: Plywood sheets that form the nailing base for roofing shingles.
Slope (or pitch): The number of inches of vertical rise of the roof over a horizontal distance of 12 inches; a “4 in 12” roof has a slope that rises 4 inches over a 12-inch run.
Soffit: The underside of the rafters and roof at the eaves.
Square: Unit of measure equal to 100 square feet, used as a basis for measuring roof area. Also, the amount of roofing material, allowing for overlapping, needed to cover 100 square feet of roof.
Underlayment: The material, usually asphalt-saturated roofing felt or synthetic underlayment, used to cover deck sheathing before the roof surface is put down.
Valley: The junction where two downward slopping roofs meet at an angle; an important channel for water runoff.
